 İNGİLİZCE'YE DAİR HER ŞEY...
İNGİLİZCE'YE DAİR HER ŞEY...
WORD ORDER
İNGİLİZCE SÖZCÜK DİZİMİ HAKKINDA TEMEL BİLGİLER
İngilizce cümle yapısı fazla esnek değildir. Bu İngilizce’nin daha kolay bir dil olmasını sağlamaktadır.
İşte Türkçe ve İngilizce örnekler.
- Mehmet arabayı dün tamir etti.
- Dün arabayı Mehmet tamir etti.
- Dün Mehmet arabayı tamir etti.
- Arabayı dün Mehmet tamir etti.
Gördüğümüz gibi Türkçe’de vurgulanmak istenen cümle öğesinin yeri değiştirilebilir. Ancak İngilizce’de bu esneklik yoktur.
Mehmet repaired the car yesterday.
İngilizce’de cümle öğelerinin yerlerinin bazı durumlarda değiştiğini göreceğiz. Bu durumlarda özel ekler, noktalama işaretleri gibi değişiklikler gerekecektir.
PASSIVE VOICE (EDİLGEN YAPI)
The car was repaired by Mehmet yesterday.
ZAMAN İFADELERİNİN CÜMLENİN BAŞINDA KULLANILMASI
Yesterday, Mehmet repaired the car.
DEVRİK CÜMLELER
Never does she come here.
CÜMLENİN ÖĞELERİ
- İsim (Noun) →Özne ve nesne
- Fiil (Verb) →Cümlede gerçekleşen eylem
- Sıfat (Adjective) → İsimleri niteleyen kelimeler ve yapılar
- Zarf (Adverb) → Bir eylemin nasıl, nerede, ne zaman yapıldığını bildiren ifadeler ve kelimeler.
- Zamir (Pronoun) → İsimleri yinelememek amacıyla isimlerin yerine kullanılan kelimeler
- İlgeç (Preposition) →in, on, at, vb. gibi kelimeler
- Belirteçler (Articles) → the, a, an, some, vs gibi isimlerin önünde kullanılan kelimeler.
- Tamlama (Phrase) → En az iki kelimeden oluşan ve tek öğe görevi olan yapılar.
- Cümlecik (Clause) → Kendi öznesi, fiili ve diğer öğeleri olan ancak tek başına anlamı olmayan ve cümle öğesi görevi olan yapılar.
- Bağlaçlar (Conjunctions) → Cümle öğelerini ve iki cümleyi birbirine bağlama görevi olan kelime ve ifadeler.
CÜMLEDE ÖZNE
Jane is at work.
She is at work.
The man is over there.
The old woman is in the room.
The man who lives next door is John’s uncle.
Whether the woman knows the answer in important.
CÜMLEDE NESNE
I saw Tina yesterday.
I saw her yesterday.
I saw the girl yesterday.
I saw the girl whose father works for this company.
I gave Mary a present.
I gave a present to Mary.
I told the old man to phone me later.
I know where she lives.
I know that she knows everything.
CÜMLEDE PREPOSITION
YER, KONUM BİLDİRME
I met them at school.
She is in her office.
I saw him on the bus.
SIFATLAR İLE KULLANIM
She is interested in music.
I am good at playing football.
PHRASAL VERBS
I looked at them.
I looked for them.
I looked after them.
CLAUSES (CÜMLECİKLER)
ADVERBIAL CLAUSES (ZARF CÜMLECİKLERİ)
I left home when they phoned me.
I left home as soon as they called me.
She phoned me as I was leaving home.
I did not go out because it was wet and windy.
ADJECTIVE CLAUSES (SIFAT CÜMLECİKLERİ)
They told me about the man who robbed the bank.
They told me about the car which they bought last month.
NOUN CLAUSES (İSİM CÜMLECİKLERİ)
Could you tell me where the accident happened?
Could you tell me whether she knows anything about the accident?
Nobody knows that she is my cousin.
TEMEL CÜMLE YAPILARI
Genel olarak iki tip cümleden bahsedebiliriz.
- İsim cümlesi
- Fiil cümlesi
İsim cümlesi to be fiili kullanılarak oluşturulur. Farklı amaçlar için kullanılır ve kesin hüküm verir. Bilim dili olduğunu da ekleyebiliriz.
Bacteria are both harmful and beneficial.
Semantics is the study of meaning.
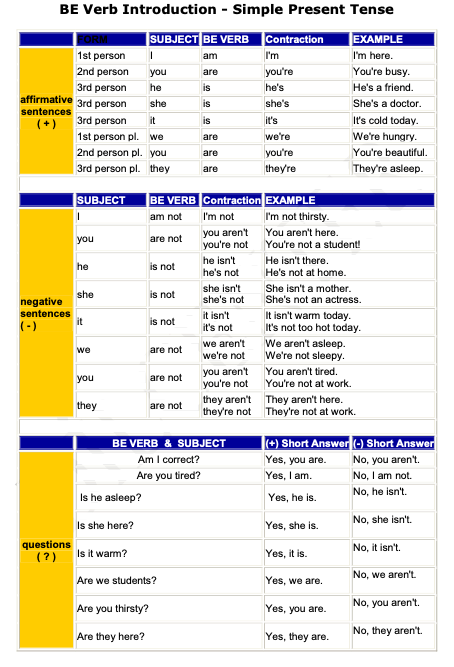
Diğer bütün fiillerde olduğu gibi to be fiilinin de 3 farklı çekimi vardır.
PRESENT PAST PAST PARTICIPLE
Be = am, is, are was, were been
BE Verb Introduction- Simple Past Tense
|
|
FORM |
SUBJECT |
BE VERB |
EXAMPLES |
|
|
Affirmative |
1st person |
I |
was |
I was in Ankara last weekend. |
|
|
2nd person |
You |
were |
You were a student ten years ago. |
||
|
3rd person |
He |
was |
He was sad this morning. |
||
|
3rd person |
She |
was |
She was very tired last Sunday. |
||
|
3rd person |
It |
was |
It was very hot yesterday. |
||
|
1st person pl. |
We |
were |
We were at school in the morning. |
||
|
2nd person pl. |
You |
were |
You were students ten years ago. |
||
|
3rd person pl. |
They |
were |
They were with us the day before yesterday. |
||
|
|
SUBJECT |
BE VERB |
Contraction |
EXAMPLES |
|
|
Negative |
I |
was not |
wasn’t |
I was not here two days ago. |
|
|
You |
were not |
weren’t |
You were not at school yesterday. |
||
|
He |
was not |
wasn’t |
He was not a student last year. |
||
|
She |
was not |
wasn’t |
She was not tired when I saw her. |
||
|
It |
was not |
wasn’t |
I was not rainy last weekend. |
||
|
We |
were not |
weren’t |
We were not İn Şanlıurfa last month. |
||
|
You |
were not |
weren’t |
You were not with us yesterday. |
||
|
They |
were not |
weren’t |
They were not here three months ago. |
||
|
|
BE VERB & SUBJECT |
(+) Short answer |
(-) Short answer |
||
|
Questions |
Was I correct? |
Yes, you were. |
No, you weren’t. |
||
|
Were you tired? |
Yes, I was. |
No, I wasn’t. |
|||
|
Was he asleep? |
Yes, he was. |
No, he wasn’t. |
|||
|
IWas she here? |
Yes, she was. |
No, she wasn’t. |
|||
|
Was it warm? |
Yes, it was. |
No, it wasn’t. |
|||
|
Were we students? |
Yes, you were. |
No, you weren’t. |
|||
|
Were you thirsty? |
Yes, we were. |
No, we weren’t. |
|||
|
Were they here? |
Yes, they were. |
No, they weren’t. |
|||
BE Verb Introduction – Present Perfect Tense
|
|
FORM |
SUBJECT |
BE VERB |
Contraction |
EXAMPLE |
|
Affirmative |
1st person |
I |
have |
I've |
I've been here since 10. |
|
2nd person |
You |
have |
You’ve |
You've been busy lately. |
|
|
3rd person |
He |
has |
He’s |
He's been there since then. |
|
|
3rd person |
She |
has |
She’s |
She's been a doctor for a year |
|
|
3rd person |
It |
has |
It's |
It's been cold since yesterday. |
|
|
1st person pl. |
We |
have |
We’ve |
We've been hungry since 1. |
|
|
2nd person pl. |
You |
have |
You’ve |
You've been here since last week. |
|
|
3rd person pl. |
They |
have |
They’ve |
They've been asleep for an hour. |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
SUBJECT |
BE VERB |
Contraction |
EXAMPLE |
|
|
Negative |
I |
have not |
I’ve not I haven’t |
I haven’t been her efor a long time. |
|
|
You |
have not |
You haven’t |
You haven’t been here for a long time. |
||
|
He |
has not |
He hasn’t |
He hasn’t been at work since then. |
||
|
She |
has not |
She hasn’t |
She hasn’t been in London for two years. |
||
|
It |
has not |
It hasn’t |
It hasn’t been warm for three days. |
||
|
We |
have not |
We haven’t |
We haven’t been busy since yesterday. |
||
|
You |
have not |
You haven’t |
You haven’t been tired since you came here. |
||
|
They |
have not |
They haven’t |
They haven’t been here since 2010. |
||
To be fiilini kullanabileceğimiz belli başlı alanladan örnekler:
MESLEK
John is a lawyer.
They are students.
TANIM
Tony is a student.
Iron is solid.
The world is round.
YER VE KAYNAK GÖSTERME
Gary is at home/on the plane/in his Office/in front of the car.
Tina is upstairs/downstairs/here/there/inside/outside.
They are from Ankara.
DURUM, GÖRÜNÜM, ÖZELLİK, RENK, UYRUK BİLDİRME
She is tired.
They are happy.
He is handsome.
Mary is beautiful.
Tony is generous and helpful.
My car is black.
They are Japanese.
THERE + BE
There is a museum in Şanlıurfa.
There are a lot of good restaurants in Istanbul.
There was an old building here ten years ago.
There were three men outside o couple of minutes ago.
There has been a financial cricis for the last three months.
There have been serious problems all over the country since last year.
WORD ORDER IN ENGLISH / İNGİLİZCE’DE. SÖZCÜK. DİZİLİŞİ
|
6 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
When? |
Who? Which? What? |
Action |
Who? Which? What? |
How? |
Where? |
When? |
Why? |
|
|
I |
like |
music. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
We |
saw |
the accident. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
We |
saw |
the accident. |
|
|
yesterday. |
|
|
Yesterday, |
we |
went |
|
|
to the movies. |
|
|
|
|
I |
Did not like |
the movie. |
|
|
|
because it was boring. |
|
|
A man |
was talking |
|
loudly. |
|
|
|
Yani sıralamayı başka şekilde açıklayacak olursak şöyle sıralama yapılır.
Subject Verb Object Manner Place Time Reason
Özne Fiil Nesne Durum Zarfı Yer Zarfı. Zaman Zarfı Neden
S V O M P T
Daha fazla örnek
Gary called me yesterday.
The bus returned late last night.
John had breakfast at 7.
The bus hit a tree.
The bus colliced with a tree.
John called earlier to cancel his appointment.
John ate breakfast on the train this morning because he was late.
The bus returned to the station to drop off the passengers.
The bus hit the tree with great force.
DIFFERENT ELEMENTS OF TIME/ ZAMAN ZARFLARININ SIRALAMASI
They arrived at the hotel at 11 a.m. on Thursday last week.
DIFFERENT ELEMENTS OF PLACE / YER ZARFLARININ SIRALAMASI
They live in a small flat in a big city in Ankara.
YER ZARFINI VURGULAMA (YER ZARFI CÜMLE BAŞINDA)
On the train, John ate his breakfast. (Unnatural)
On the train, John was fine, but at the office, he felt sick.
ZAMAN ZARFINI VURGULAMA (ZAMAN ZARFI CÜMLE BAŞINDA)
Earlier, John called to cancel his appointment.
Earlier, John felt sick, but now, he is allright.
HOW AT THE BEGINNING OF A SENTENCE
With great force, the bus hit the tree. (Unnatural)
The bus swerved, and with great force, hit the tree.
WHY AT THE BEGINNING / NEDENİN. VURGULANMASI
To drop off the passengers, the bus returned to the station. (UNNATURAL)
To drop off the passengers safely, the bus returned to the station.
POSITION OF ADVERBS / ZARFLARIN KONUMU
FREQUENCY ADVERBS / SIKLIK. ZARFLARI
I always watch the news.
I do not always watch the news.
I can’t always watch the news.
They will never do that again.
He hardly ever goes out.
She can rarely have a rest.
She occasionally writes to me.
He sometimes has to work late.
She doesn’t usually work on Fridays.
I have often seen him.
ALREADY, RECENTLY, JUST, FINALLY, SOON, STILL, ALMOST, ALL, CURRENTLY, ALSO, PROBABLY, BOTH, EVEN, HARDLY
I have already had lunch.
They have recently bought a new car.
She has just come back.
We finally managed to contact him.
We will soon have a break.
He is still watching television.
I almost forgot.
They have all finished.
They are currently negotiating a deal.
I would also like to visit the museum.
We will probably go on holiday next week.
We both arrived late.
I can’t even move my fingers.
I could hardly hear him.
WHEN TO BE IS THE MAIN VERB OF THE SENTENCE /TO BE CÜMLENİN ASIL FİİLİ İSE
She is always here.
The bus is rarely on time.
They are often tired.
We were all happy.
August was even hotter than July.
I am already late.
PUTTING AN ADVERB AT THE BEGINNING OF A SENTENCE IN ORDER TO EMPHASIZE IT
VURGU AMACIYLA. ZARFIN CÜMLE BAŞINDA YER ALMASI
Sometimes, he has to work late.
Usually, she doesn’t work on Fridays.
Finally, we managed to contact him.
Soon, we will have a break.
Currently, they are negotiating a deal.
NEGATIVE ADVERBS AT THE BEGINNING OF A SENTENCE REQUIRE INVERSION
CÜMLE BAŞINDA BULUNAN OLUMSUZ. ZARF DEVRİK YAPI GEREKTİRİR
Never will they do it again.
Rarely can she have a rest.
Seldom does it rain here.
ADVERBS OF MANNER
He opened the door quietly.
He quietly opened the door.
We could see it in the distance clearly.
We could clearly see it in the distance.
She was singing happily.
She was happily singing.


